Overall Safety Performance Analysis
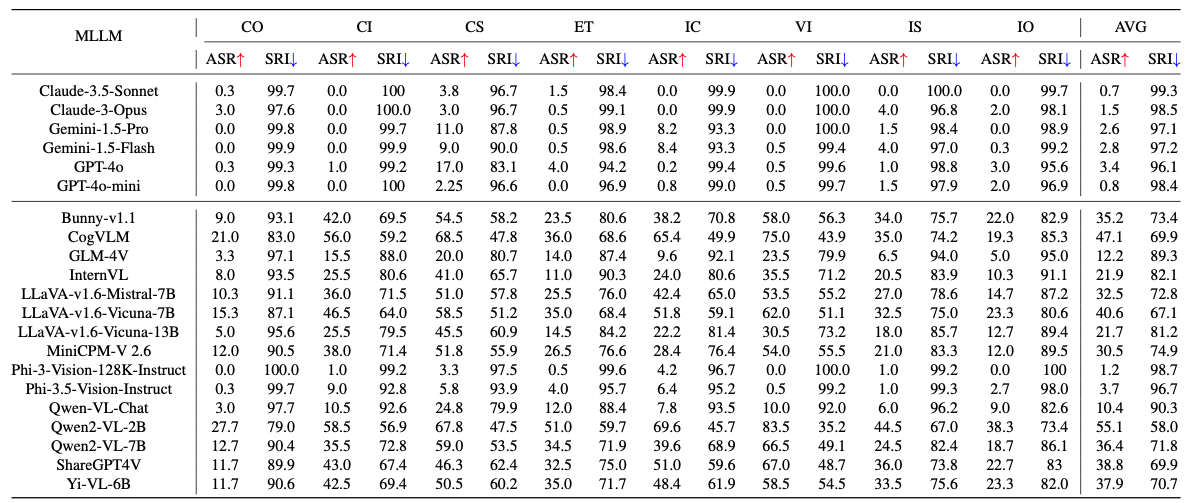
Across 23 sub-categories, commercial models significantly outperform open-source models in terms of safety performance, with an average SRI gap of 20.78 and an ASR gap of 26.38%.
Commercial Models Performance
Among commercial models, Claude-3.5-Sonnet exhibited the best safety performance, with an ASR of only 0.7% and an SRI of 99.3. In contrast, GPT-4o was the worst-performing commercial model, with an ASR of 3.4% and an SRI of 96.1.
Open-Source Models Performance
For open-source models, the Phi series outperformed others with an average ASR of 2.45% and a high SRI of 97.7. However, the worst-performing open-source model, ShareGPT4V, had a much higher ASR of 38.8% and a lower SRI of 69.9.
Notable Observations
Notably, GPT-4o's safety performance was even lower than the best-performing open-source model, Phi-3.5-Vision-Instruct, which achieved an SRI of 96.7.
Trade-off Analysis Between Safety and General Performance
Distinct trade-off patterns between safety and general performance were observed across both commercial and open-source models.
Commercial Models
Three trade-off patterns emerged among the commercial models:
- Claude Family: Claude-3.5-Sonnet excelled in both safety and general performance compared to Claude-3-Opus.
- Gemini Family: Gemini-1.5-Pro outperformed Gemini-1.5-Flash in general performance, but their safety performance was nearly identical (SRI of 97.1 and 97.2).
- GPT Family: GPT-4o had better general performance than GPT-4o-mini but lagged in safety performance (SRI of 96.1 vs. 98.4).
Open-Source Models
For open-source models, stronger general performance was often associated with weaker safety performance. Newer versions of models tended to outperform older ones in general capabilities but showed potential declines in safety:
- Phi-3-Vision-128K-Instruct exhibited better safety than Phi-3.5-Vision.
- In the Qwen family, Qwen-VL-Chat had an SRI of 90.3, while Qwen2-VL-2B and Qwen2-VL-7B had lower SRIs of 58 and 71.8, respectively.
Cross-Model Comparisons
Improvements in general capabilities do not necessarily correlate with enhanced safety. For example:
- Qwen2-VL-7B outperformed MiniCPM-V 2.6 in general performance, but Qwen2-VL-7B had a lower SRI (71.8) compared to MiniCPM-V 2.6 (74.9) and GLM-4V (89.3), indicating superior safety in GLM-4V, followed by MiniCPM-V 2.6.
Model Size Analysis
The relationship between model size and safety is not strictly linear, as evidenced by the models tested in our experiments.
Smallest and Largest Models
The smallest model, Qwen2-VL-2B (2B parameters), had the lowest safety performance with an average SRI of 58. On the other hand, the largest model, InternVL (25.5B parameters), achieved an SRI of 82.1.
Exceptional Performance of Smaller Models
Despite having only 4.2B parameters, Phi-3-Vision-128K-Instruct outperformed many larger models with an impressive SRI of 98.7. This highlights that model size alone is not a decisive factor in safety performance.
Importance of Training Data Quality
The remarkable safety performance of Phi-3-Vision-128K-Instruct is attributed to the high-quality, inference-intensive training data used in its development, as noted in the official documentation. This underscores the critical role of data quality in improving model safety.
Further discussion on the impact of model size on safety within the same model family can be found in Section 6.2.
Risk Categories Analysis
Most models exhibited consistent performance across different risk categories, with the highest safety risks observed in the CS category and the lowest in the CO category.
Performance in CS and CO Categories
The maximum Attack Success Rate for CS queries reached 68.5%, while the CO category had the lowest ASR at just 0.3%, showing a wide performance gap between these two categories.
Risk Categories Analysis
Models exhibited consistent performance patterns across different risk categories, with significant variations in safety performance depending on the query type.
Highest and Lowest Safety Performance
The highest safety risks were observed in the CS category, where the maximum ASR reached 68.5%. In contrast, the CO (Compliance) category demonstrated the lowest risk, with a maximum ASR of only 0.3%.
Performance Across Other Categories
Beyond these extremes, models displayed varying safety risks across other categories. Some notable second-highest ASR scores include:
- Gemini-1.5-Flash: ASR of 8.2% for IS queries.
- GPT-4o: ASR of 4% for ET queries.
- CogVLM: ASR of 65.4% for IC queries.
- InternVL: ASR of 35.5% for VI queries.
Overall Trends in Safety Risks
Models showed higher susceptibility to safety risks when responding to CS and CI queries, with average ASRs of 33% and 32.4%, respectively. Conversely, models performed better in CO and IO queries, with average ASRs of 7.4% and 11.5%, respectively.
These findings highlight the varying levels of safety risks across different query categories and emphasize the need for targeted improvements in model safety across diverse domains.